Energy compliance can often feel like a balancing act. While the SBEM (Simplified Building Energy Model) is a widely used tool for compliance with Part L of the Building Regulations, it’s designed to streamline calculations, which means it has inherent limitations. For more complex or unique buildings, Dynamic Simulation Modelling (DSM) steps in to offer a much more detailed and realistic picture of energy performance.
This article explains DSM’s role, how it differs from SBEM, and why it’s the preferred method for certain projects.
What Is DSM?
Dynamic Simulation Modelling is a detailed and dynamic approach to energy modelling that simulates a building’s performance on an hour-by-hour basis. Unlike SBEM, which relies on broad averages and simplified inputs, DSM incorporates specific details about weather, geometry, materials, and systems to produce an accurate and nuanced analysis.
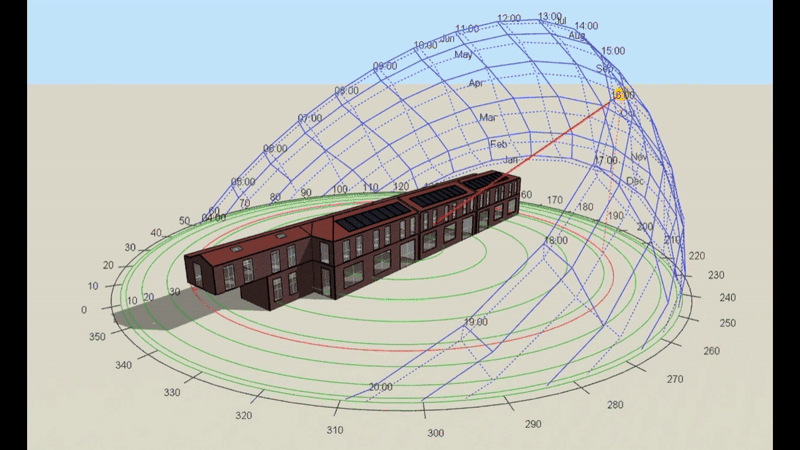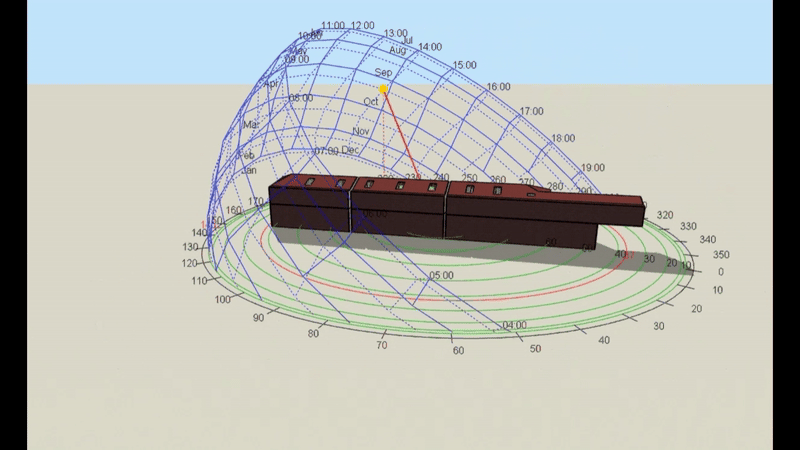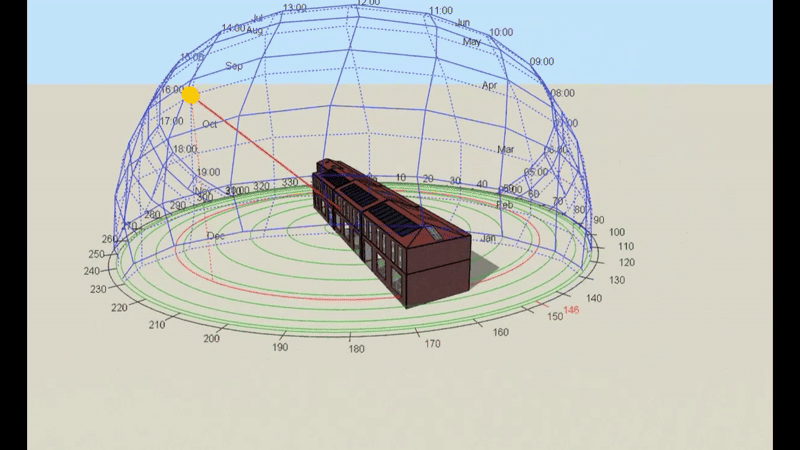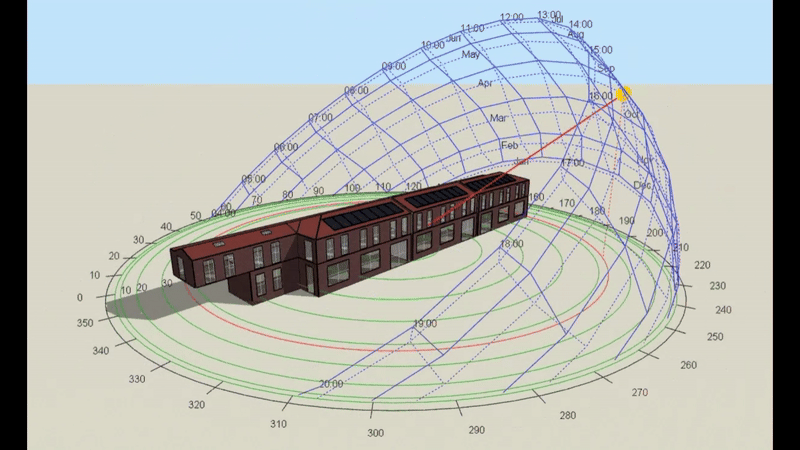
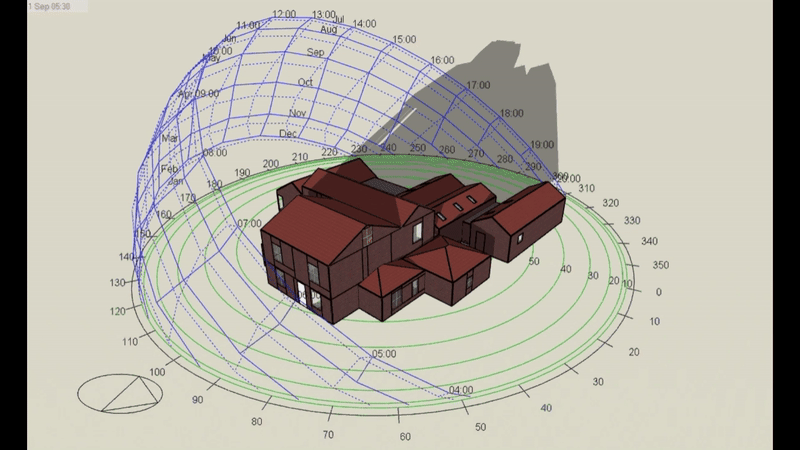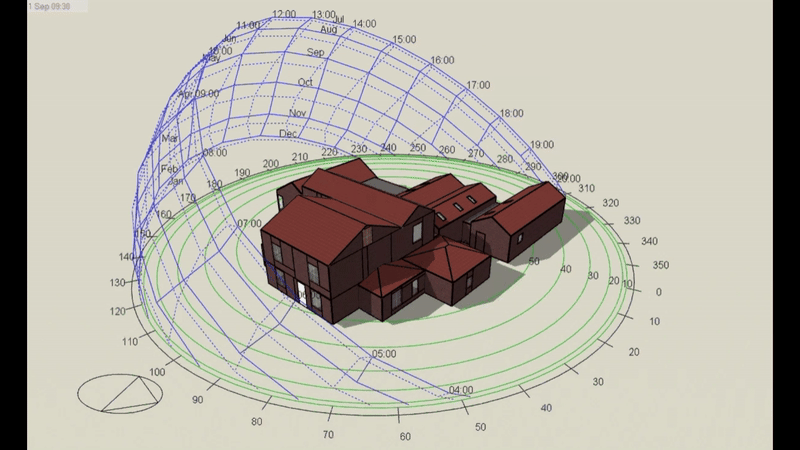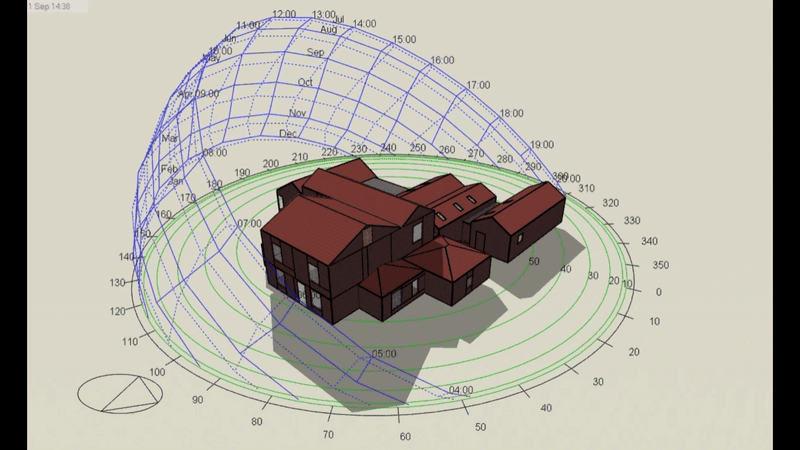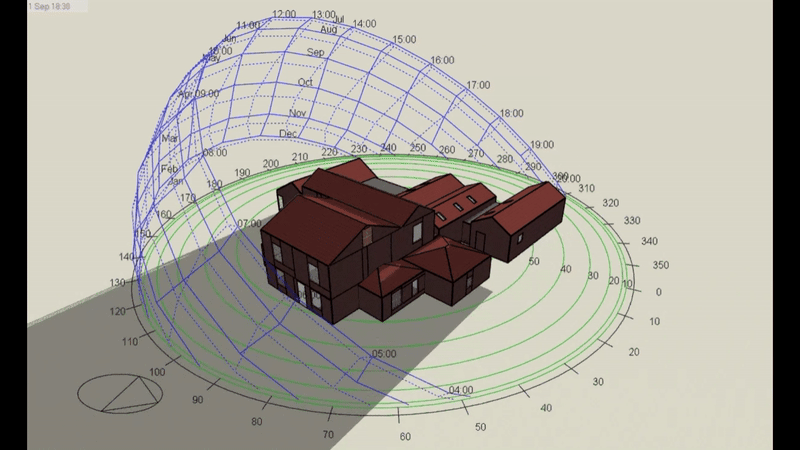
DSM is particularly relevant for Level 5 buildings, which include complex structures and those requiring precise energy compliance data. However, it’s important to note that Level 5 calculations can be performed on any building, regardless of its complexity, if a more detailed assessment is required or desired. This flexibility makes DSM a powerful tool for a wide range of projects.
How Does DSM Differ from SBEM?
1. Weather Data
- SBEM: Uses monthly average weather data, offering a generalised view of energy use.
- DSM: Incorporates hourly weather data, capturing fluctuations in temperature, solar radiation, and wind conditions throughout the day and year. This enables precise modelling of heating and cooling demands under different scenarios.
2. Building Geometry
- SBEM: Simplifies layouts and assumes standard configurations, which can miss key details in complex designs.
- DSM: Accurately models intricate features, including atriums, internal openings, and irregular shapes. It also accounts for inter-zone heat transfer, providing a realistic representation of thermal performance.
3. Shading and Solar Gains
- SBEM: Considers shading as a fixed factor, offering limited insight into its impact.
- DSM: Analyses shading dynamically, calculating the effects of features like louvres, overhangs, or blinds across different times of the year. This allows for a more accurate prediction of cooling loads.
4. Daylighting and Controls
- SBEM: Lacks the capability to assess daylighting systems in detail.
- DSM: Models daylighting controls, which adjust artificial lighting based on natural light levels. By factoring in window orientation, glazing, and shading, DSM evaluates how these controls reduce energy consumption and improve occupant comfort.
5. Heat and Light Movement
DSM captures how heat and light move between zones, factoring in inter-zone thermal exchanges. This level of detail is crucial for buildings with open-plan layouts, shared spaces, or atriums where conventional models might fall short.
Why Use DSM?
Accuracy in Complex Designs
DSM provides a detailed and realistic assessment of energy performance, particularly for buildings with non-standard features. This is essential for ensuring compliance with Part L and offers confidence that the design will meet energy efficiency targets.
Regulatory Requirements
Level 5 buildings must use DSM for compliance with Part L of the Building Regulations. This includes projects with complex geometries, large-scale glazing, or advanced HVAC systems that SBEM cannot adequately model.
Cost Implications and Mitigation
DSM assessments and Level 5 EPCs can cost more than SBEM-based evaluations. However, the detailed insights DSM provides often lead to better design decisions that reduce long-term energy costs. For example, DSM can optimise HVAC systems or shading strategies, resulting in energy savings that offset the initial expense.
Applications Beyond Compliance
DSM isn’t just about ticking regulatory boxes. It’s a tool for improving building performance. By simulating various scenarios, DSM helps developers make informed decisions about materials, systems, and layouts.
When Is DSM Essential?
DSM is particularly valuable for:
- Atriums: Accurately modelling thermal performance and airflow in large, open spaces.
- Daylighting Controls: Evaluating energy savings from natural light strategies.
- Shading Systems: Analysing the effectiveness of fixed or dynamic shading devices.
- Large Commercial Buildings: Managing complex HVAC systems and extensive glazing.
- High-Performance Projects: Where achieving ambitious energy targets is critical.
The Nuance of DSM
While DSM offers significant advantages, interpreting the data and optimising designs effectively requires specialist expertise. DSM also relies on high-quality input data, because errors in assumptions about materials or systems can impact the accuracy of results.
Additionally, DSM isn’t focused on producing higher EPC ratings; instead, it provides an accurate assessment of energy use, highlighting areas for improvement. This makes DSM a valuable tool for refining designs rather than chasing scores.
DSM offers a level of detail and accuracy that SBEM cannot match, making it essential for complex or high-performance projects. While it comes with a higher upfront cost, the insights it provides often lead to significant long-term benefits, from energy savings to enhanced occupant comfort. Plus, with its flexibility, DSM can be applied to any building, regardless of size or complexity, to achieve the most accurate energy assessment possible.
For projects that demand more than basic compliance, DSM is the clear choice. Ready to take your project to the next level? Contact us today to get a tailored quote and learn how DSM can optimise your design and compliance journey.
Get a Quote
For a precise estimate tailored to your project, Get A Quote


